ExSpiron
Measuring and trending minute ventilation in non-intubated patients
The first and only non-invasive monitor for monitoring the tidal volume, respiratory rate and minute volume:
“NEVER MISS A BREATH”.
Minute ventilation is the amount of air someone breathes in a minute. A change in minute ventilation is the first indication of respiratory deterioration. Methods for accurate non-invasive monitoring of changes in respiratory status are limited.
ExSpiron enables non-invasive Respiratory Volume Monitoring (RVM), which has been demonstrated to provide the most direct measurement of respiratory status and the earliest indicator of changes in respiratory status.
Description
EARLY, ACCURATE AND RELIABLE INFORMATION
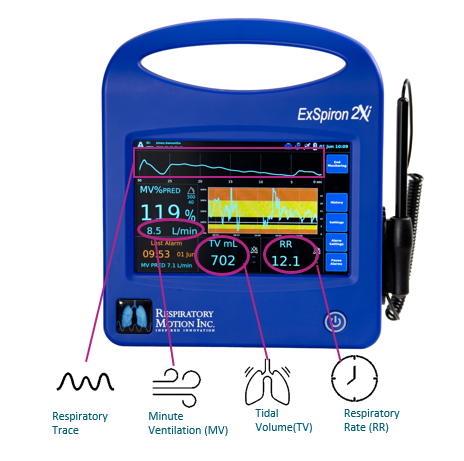
The ExSpiron 2Xi is a compact patient monitor that delivers real-time, continuous measurements of noninvasive minute ventilation, providing clinicians with the essential information needed to provide optimal patient care.
Minute volume (MV) is the volume moved by the lungs in 1 minute. It is the most direct measure of respiratory status and is therefore THE first indicator of respiratory distress. Changes in Minute Ventilation and tidal volume often precede life-threatening hyperventilation, hypoventilation, or apnea. Early detection enables early intervention, reducing risk to the patient.
Monitoring of tidal volume has been shown to provide the most direct measure of respiratory status and the early indicator of changes in respiratory status. This additional vital parameter (respiratory volume) is: Fast – It identifies the first signs of impaired respiratory function, up to 60 minutes earlier. Easy to use - Non-invasive and comfortable for both adults and children.
With 100 times fewer false alarms, ExSpiron™ also reduces patient monitoring work and alarm stress. Cost effective – Faster respiratory intervention (71 minutes) can occur, avoiding additional interventions and reducing costs. Preventive - Monitoring of minute ventilation provides the earliest indication of change in respiratory status in non-intubated patients and intubated or cannulated patients in the supine position, spontaneous breathing, or late weaning. Respiratory problems increase patient mortality by more than 30% and intensive care stays by around 50%. With the ExSpiron™, we enable clinicians to quickly, accurately and continuously assess a patient's respiratory status for safer and more cost-effective care.
Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring with the ExSpiron is supported by clinical evidence from > 6,000 patients and > 1 million data points.
THE EXSPIRON OFFERS MANY BENEFITS
The ExSpiron™, is a lightweight monitor with PadSets, which continuously displays the patient's real-time tidal volume, respiratory rate and minute ventilation volume.
The PadSet is:
• Comfortable for the patient
• Available in adult and child sizes
• Customizable size per patient (single use).
• Easy to install and attach
• Can remain in place for 24 hours without being replaced
• Radiation permeable, for use with X-rays
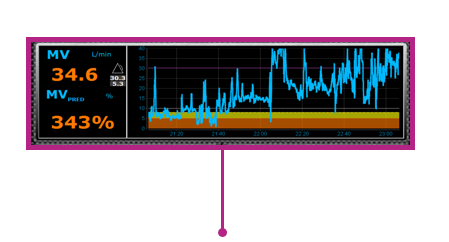
The ExSpiron uses the patient's height, gender and weight to calculate a predicted minute ventilation, which is the patient's breathing at rest. This is defined as the 100% Predicted Minute Ventilation (MVPRED). ExSpiron continuously measures and displays the patient's VC, RR and MV in real time, using data from the PadSet. The monitor displays all measured parameters as a number and a trend.
SUITABLE FOR VARIOUS CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Emergency room
• Minute ventilation alerts you early to breathing problems so you can decide when to change or adjust therapy (high flow settings, start NIV, extubate or intubate).
• Simple monitoring of overall respiratory status makes waiting patients easier and safer admission or to be monitored in the observation units. Post Anesthesia Care Unit
• Monitoring of minute ventilation provides the first warning of changes in respiratory status. • Reduces post anesthesia care dwell time from 3 hours to 1.7 hours.
• Let patients return to their rooms with confidence, even those with hard-to-assess OSA.
Intensive care
• Reliable assessment of the need for re-intubation can reduce ventilation time.
• Estimated savings of 1.5 to 2 days on a mechanical re-intubation ventilator.
• Shortened length of stay in intensive care.
• More clarity on tidal volume, respiratory rate, and minute volume when using a high-flow nasal cannula
Procedural sedation and analgesia
• Tidal volume monitoring detects changes in respiratory and ventilation status on average 71 minutes faster than with SpO2.
• Added security for post-operative monitoring of high-risk pulmonary and OSA patients.
General Services
• Confidence in the need for non-invasive positive pressure ventilation.
• A clear view of ventilation in a breathing mask situation, High flow etc...